The Proven Laws of User Experience (UX) Design
Whether you are an experienced designer or a fresher just making your way in the design world, crafting user-friendly and intuitive designs can be challenging without a comprehensive understanding of design principles.
Design laws serve as the building blocks of the design process, much like the alphabet in English. Just as you cannot modify the letters, design laws provide the foundational rules to follow and maintain industry standards to deliver a seamless user experience.
Today I will share some of the proven laws of user experience that can help you enhance user satisfaction and improve your conversion rates. So without further ado, let's dive in.
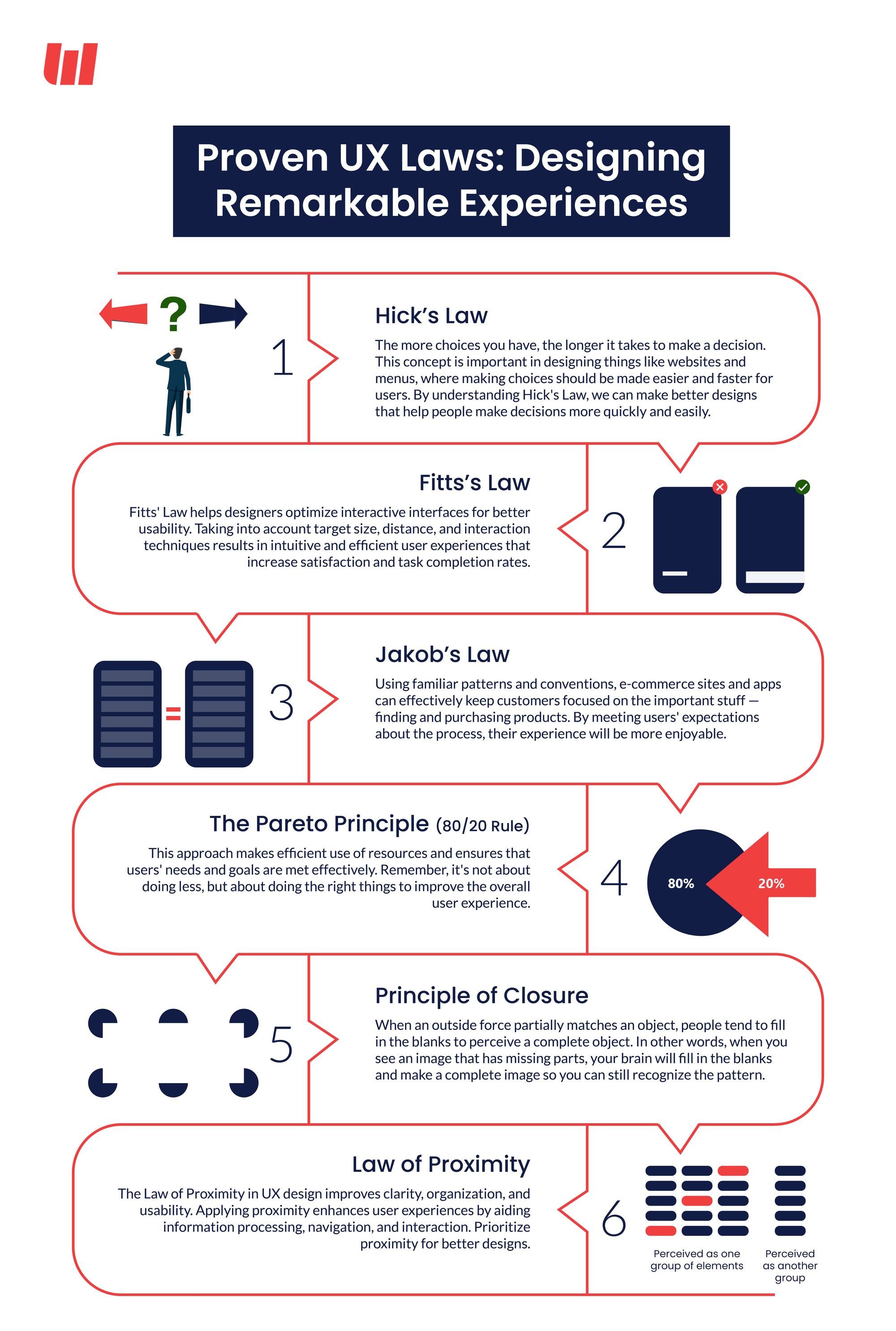
Hick's Law
Have you ever found yourself getting confused when you have too many choices?
Suppose you go to Shop 1 to buy a grinder, and the salesperson shows you five different models. Then you go to Shop 2, and the salesperson shows you just two grinders. You will likely take longer to decide at Shop 1 because of the more choices available. This phenomenon is known as Hick's law.
Hick's law is named after renowned psychologists William Edmund Hick and Ray Hyman. So it is also named the Hick-Hyman Law. It states that the relationship between the number of choices and the time consumed to make a decision is directly proportional.
In short, more choices mean more complexity and decision-making time. The main aim of a great design is to reduce the decision-making time and the response time for users, and by applying Hicks law, you can achieve that.
How can Hick's law be applied in UX Design?
Hick’s law can be applied in various ways. It includes:
Easy navigation
When you are looking for a particular option, you want to reach it in minimal steps. Keeping a clear and concise menu can effortlessly help your users find what they are looking for with the least downtime.
Limited options
By limiting the number of choices, you can eliminate confusion and help users make decisions more quickly.
Clear call-to-action
Keep a few CTAs with an inspiring design that motivates users to click.
Share information on the progress
Don't share everything at once. Share information as the user progresses so that the user can focus on one thing at a time.
Highlight important content
Decide on what's essential that you want your user to know and highlight it for attention.
Fitts's Law
Fitts's law is a fundamental principle that strongly influences UX design. It states that the time taken to reach a target is directly related to its distance and inversely related to its size. In short, a target that is larger and closer will be easier to reach than one that is smaller and farther away. Psychologist Paul Fitts introduced it in 1954.
As per Fitts's law, making interactive buttons larger, especially for handheld devices, can enhance the user experience. As per Fitts's law, larger interactive buttons can ease the user's pain and make it less time-consuming.
How does Fitts's Law affect UX Design?
Fitts's law has various applications, which include:
Size constraint
Size does matter. Design experts state that larger targets are easier to click than smaller ones. So the designers must go for larger buttons that are easy to click.
Decreased proximity
If you know that a user has frequent interactions with a button or an element, keep it closer to their reach. This can help reduce unnecessary movement and boost efficiency.
Group-related elements
Place the elements that have more interaction with each other closer so that the user doesn't have to travel much for the second interaction after making the first.
For example, If you have a form with different fields, a submit button should be close to the last field, so that the user can immediately click on it.
Consider user-device compatibility
Ensure that the elements you design are compatible with all the devices. Test it on different devices to get clarity.
Jakob's Law
Usability expert Jakob Nielsen coined Jakob's Law. It states that the users expect similar behavior from your website or app as from other similar websites or apps. It makes their interaction smooth. For example, if you are designing a website similar to Amazon, it should work in a similar way to ease user interaction.
It eliminates the need for learning and getting used to a completely new experience for users.
When a user switches to a new website, they carry with them their prior experiences, so they look for similar experiences. By incorporating common standards and practices, designers can enhance users' experiences.
Here's how Jakob's Law can be effectively applied in UX design:
Consistent navigation
Keep a uniform navigation layout throughout your website or application. Users must be able to get important elements at similar locations.
Standard icons
Use common icons used globally for normal actions like home, settings, and sharing. Don't use customized icons that can confuse users.
Responsive design
Make sure your design is compatible with different devices.
Error handling
Follow the same error handling procedure as is followed in your industry. The errors should be clear and concise for users to understand.
It uplifts overall user satisfaction by reducing the learning curve associated with a new platform.
The Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule)
The Pareto Principle is also called the 80/20 rule. Now why is it called 80/20?
Well. It states that 80% of the results come from 20% of the efforts, so it is named the 80/20 rule. It came into the picture when Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto observed that 20% of the population in Italy owns around 80% of the land. Today, it's applied to different fields, including business, economics, and productivity.
How can the Pareto principle be applied in UX Design?
It highlights that a major part of the user experience is dependent on a few essential elements. It can be core features, user interactions, or specific design elements that strongly influence the overall user satisfaction and success of a digital product.
Prioritize your features
Segregate the 20% of features holding higher value for your users and optimize their design and experience to meet their needs and goals.
User research
Identify the major issues that 80% of your users have and resolve them for a seamless user experience.
Keep it simple
Keep the vital elements simple and easy to use. Avoid adding unnecessary elements that can distract users.
Principle of Closure
Gestalt psychology derived the principle of closure. It works on the human tendency to perceive incomplete or fragmented visual elements as complete entities. It reflects that our brains can naturally fill in the missing information to create a complete and recognizable pattern. UX Design implements it by creating engaging elements and sharing information with minimal elements. Fewer elements mean reduced complexity.
How does the closure principle work in favor of UX Design?
The closure principle is applied in:
Logo design
If you have strongly observed, logos represent visual information by using minimal elements. The closure is applied here as we use fragmented elements for the user to understand the complete representation.
Icon design
In most places, even icons are used to convey meaning with minimal visual elements.
Law of Proximity
Gestalt psychology derived the law of proximity. Under this law, It states that the objects that appear close to each other are considered one group. It holds great value in UX design as it affects how users perceive the information within a design.
How is the law of proximity applied in UX Design?
UX design applies the law of proximity by:
Grouping related elements
Put elements like buttons and related navigation items close to each other. It makes it easy for users to understand the information.
Use proper whitespace
Making appropriate use of whitespace is essential, as it helps to determine distinguishing elements and improves readability.
Content organization
When you have a lot of content, the law of proximity states that you should have similar content in one section and the rest in the other. This way, it is easier for a user to scan the complete content.
Summary
I guess by now you have a complete idea of the different laws of user experience that can help you create intuitive designs with great user experience. It can help you enhance usability, improve user engagement, boost conversion rates, and much more.
To get more insights on design services and make user-friendly designs following user experience laws, contact Logicwind. We have experts who can assist you in making a new application or enhancing your customer experience with the current application. Let's collaborate and discuss more.
FAQs
Q: What are the principle laws of UX?
A: There are certain design principles and guidelines preferred for a user-friendly experience and intuitive designs, which are called the principle laws of UX.
Q: Why are laws important in UX design?
A: UX laws are important because they serve as a foundation for intuitive, user-friendly, easily accessible, consistent, and efficient designs that enhance the user experience and interaction.
Q: How can these laws benefit UX designers?
A: These laws help UX designers improve their overall work quality and enhance the design process.
Q: Can these laws be applied to all types of user interfaces?
A: Yes, the laws of UX can be applied to all types of user interfaces, irrespective of the platform or device. Whether you are designing a website, mobile app, desktop software, or any other digital resource, these principles are standard and help to create a positive user experience.
Q: Can I apply these laws retroactively to an existing design?
A: Yes! You can retroactively apply these laws to any existing design. While it is easily possible to apply these laws to new designs, they can also be applied to existing designs to enhance the user experience.
Q: Are these laws set in stone, or can they be broken?
A: No, the principle laws of UX are not set in stone and can be broken in certain situations to achieve user needs and specific goals. It helps to create effective designs and enjoyable user interfaces.




